Introduction: My Journey to Mitochondria and Longevity
My journey into health and longevity started with genomics. Like many others in the field, I believed that understanding our genes would unlock the secrets to preventing disease. If we could decode our DNA, we could predict health risks and take proactive steps.
I spent years working on ways to bring the value of genomics into preventive healthcare. But over time, I faced a hard truth—genetics alone wasn’t enough. Just because someone has a gene linked to a disease doesn’t mean they will develop it. Genes can remain silent or be influenced by lifestyle, environment, and aging itself.
So my search for disease prevention remained unanswered. If genetics wasn’t the complete picture, what was?
That’s when I started digging deeper into what really drives disease—and I found a common thread. It wasn’t just about DNA or single risk factors. The biggest underlying cause of disease was aging itself. And at the heart of aging? Mitochondria.
Everything pointed back to how well our mitochondria function. The decline of these tiny powerhouses triggers aging, lowers energy, and increases disease risk.
When I started applying mitochondrial science, and functional medicine to my own life, the results were profound. Now, at 52 years old, I feel stronger, more energised, and healthier than I did a decade ago.
And that’s why I’m launching this mitochondria series—to share what I’ve learned, backed by the latest research, but in a way that’s practical and actionable.
This isn’t just about theory—it’s about what you can do today to protect your energy, health, and longevity. Let’s dive in.
Mitochondria
For decades, mitochondria have been primarily known for their role in producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the fuel that powers every cell in our body.
However, new research has uncovered their deeper influence on aging, metabolism, immune function, and longevity. Mitochondrial health is now recognized as a cornerstone of overall well-being and longevity.
But what happens when these tiny cellular engines decline or fail? Fortunately, emerging science shows that we can actively enhance mitochondrial function through lifestyle choices, diet, and even cutting-edge therapies.
In this article, we’ll explore:
- The critical role of mitochondria in cellular function and longevity.
- How mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to disease and aging.
- Proven strategies to optimize mitochondrial health for a longer, healthier life.
Your energy, health, and lifespan start at the cellular level—and by understanding mitochondria, you can take charge of your longevity like never before.

What Are Mitochondria and Why Are They Important?
At their core, mitochondria convert glucose and fatty acids into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the fuel that keeps your body running. But that’s just the beginning. These microscopic organelles also:
- Regulate metabolism and decide how efficiently your body uses energy.
- Control cell survival by managing apoptosis (programmed cell death)—a critical process for preventing cancer.
- Reduce oxidative stress by balancing free radicals and antioxidants.
- Communicate with the nucleus to regulate genes linked to aging, immunity, and inflammation.
In short, your mitochondrial health determines how well you age, how resistant you are to disease, and even how long you live. So the real question is—are you taking care of yours?
Mitochondria and Disease Prevention
When mitochondria are working at full capacity, you feel energetic, think clearly, and recover quickly. They fuel your body, keep inflammation low, and support cellular repair. But when they start to fail? That’s when chronic diseases creep in.
How Mitochondria Protect Against Disease?
Poor mitochondrial function has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, and cardiovascular disease.
Healthy mitochondria support cellular repair, metabolism, and detoxification. When they weaken, your body struggles with energy production and immune function, leading to conditions like Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Research shows tweaking mitochondrial fission and fusion (how mitochondria split and merge) can slow aging and improve muscle and brain health.
- Special compounds like hydrogen sulfide (mtH2S) donors protect mitochondria and delay age-related decline, making them promising anti-aging tools.
Mitochondria and Immunity
Your immune system depends on mitochondria to fight infections and control inflammation.
- Diet and fasting activate AMPK, a key enzyme that boosts mitochondrial efficiency and keeps immune cells strong.
- Hormones like insulin and IGF-1 fine-tune mitochondrial health, impacting your body’s ability to resist disease.
Simply put, strong mitochondria mean better immunity, lower inflammation, and protection from chronic illness. Up next—how they shape your lifespan and longevity.
How Mitochondria Influence Health-Span and Longevity
If you want to stay younger for longer, your mitochondria need to stay strong. These tiny powerhouses don’t just fuel your cells—they also control how fast you age.
Mitochondria and Aging
As you age, mitochondria become less efficient, leading to fatigue, weaker muscles, and slower brain function. But research shows we can slow this down:
- Boosting mitochondrial fission (splitting) in some species improves cellular repair and lifespan.
- Increasing mitochondrial fusion (merging) through dietary restriction or exercise enhances energy production and antioxidant defense.
Key Longevity Pathways
Mitochondria communicate with longevity genes that regulate aging:
- AMPK activation (triggered by fasting and exercise) strengthens mitochondria.
- TORC1 inhibition (through diet or medication) helps protect neurons and delays age-related decline.
- Insulin/IGF-1 signaling plays a role in mitochondrial quality control, keeping cells youthful.
The takeaway? Keeping mitochondria healthy can slow aging, increase energy, and extend health-span, and the right lifestyle choices can help.
How to Optimize Mitochondrial Health for Longevity
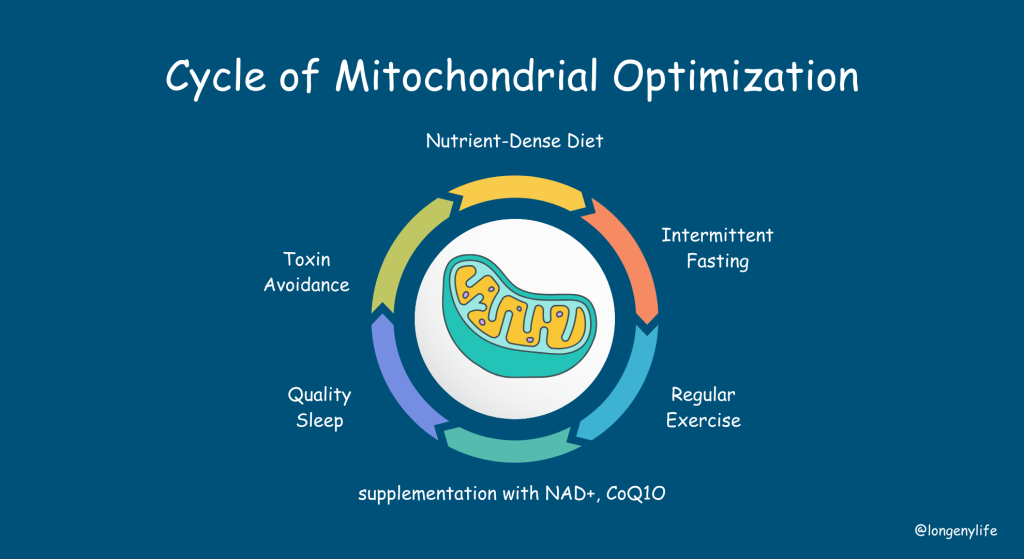
The good news? You can boost your mitochondria and slow aging with a few key lifestyle changes. Here’s how:
1. Eat for Mitochondrial Power
- Nutrient-dense foods rich in CoQ10, NAD+, and polyphenols (like berries, nuts, and dark chocolate) protect mitochondria.
- Intermittent fasting and a ketogenic diet encourage mitochondrial efficiency and energy production.
- Reducing processed foods lowers inflammation and oxidative stress, helping mitochondria function better.
2. Exercise to Build Stronger Mitochondria
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) and resistance training stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis—the process of creating new mitochondria.
- Endurance exercise enhances mitochondrial function, improving stamina and longevity.
3. Support Mitochondria with Lifestyle Choices
- Cold exposure (cold showers, ice baths) and heat therapy (saunas) stimulate mitochondrial stress responses, making them more resilient.
- Quality sleep is crucial—mitochondria repair and regenerate overnight.
- Avoiding toxins (pesticides, heavy metals, processed chemicals) helps prevent mitochondrial damage.
By making these simple changes, you can protect your mitochondria, boost energy, and extend your health-span. Next, let’s look at cutting-edge research into mitochondrial longevity.
Cutting-Edge Research on Mitochondria and Longevity
Science is always moving forward. Using the latest research, scientists are unlocking new ways to slow aging and extend health-span by targeting mitochondria. Here are some of the most exciting breakthroughs:
1. Targeted Mitochondrial Therapies
- Hydrogen sulfide (mtH2S) donors like AP39 help preserve mitochondrial function and delay aging, even when taken later in life.
- These compounds activate longevity genes (FoxO/daf-16 and GATA), rejuvenating cells and protecting against decline.
2. Rethinking the Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory
- The old belief that reactive oxygen species (ROS) drive aging is being challenged. Some long-lived species actually produce more ROS, yet still live longer.
- While mtDNA mutations increase with age, scientists are still debating whether they directly cause aging or are simply a side effect.
3. Lifestyle as Medicine
- Caloric restriction and exercise remain the most effective ways to stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and slow cellular aging.
- Researchers are exploring precision therapies that balance mitochondrial fission and fusion in different tissues to optimize aging benefits.
With these discoveries, the future of mitochondrial medicine looks promising. But for now, lifestyle choices remain the most powerful tool for protecting mitochondria and extending health-span.
Conclusion
Your mitochondria are more than just cellular batteries—they are key players in aging, disease prevention, and longevity. When they function well, you feel energetic, resilient, and healthy. But when they decline, fatigue, inflammation, and chronic disease take over.
The good news? You have the power to optimize your mitochondrial health through simple lifestyle choices:
- Eat a mitochondria-friendly diet (nutrient-rich foods, fasting, and low-processed foods).
- Exercise regularly (HIIT, strength training, and endurance workouts).
- Add dietary supplementation through NAD+, NMN, and COQ10.
Emerging research also suggests future therapies—like targeted mitochondrial compounds and genetic interventions—may soon revolutionize longevity science. But for now, your daily habits remain the best way to protect and strengthen your mitochondria.
Take care of your mitochondria, and they’ll take care of you—helping you live longer, healthier, and stronger.
Frequently Asked Questions (Faq’s)
1. How do mitochondria generate energy, and what happens when they stop working properly?
Mitochondria generate energy by converting food and oxygen into ATP, the body’s fuel. When they fail, energy production drops, leading to fatigue, aging, and disease.
2. How does mitochondrial function affect aging and the risk of diseases like diabetes and heart disease?
Healthy mitochondria keep cells energized and functioning optimally. As they decline, cells lose efficiency, leading to inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular issues—key drivers of aging and chronic disease.
3. What lifestyle and dietary changes can improve mitochondrial health and slow down aging?
Regular exercise, intermittent fasting, a nutrient-rich diet (with CoQ10, omega-3s, and polyphenols), quality sleep, and stress management all enhance mitochondrial function, boosting energy and slowing aging.
4. How do environmental factors and epigenetics influence mitochondrial function and disease progression?
Toxins, poor diet, stress, and inactivity trigger oxidative stress and epigenetic changes that impair mitochondrial function. This disruption accelerates aging and increases susceptibility to metabolic, neurodegenerative, and cardiovascular diseases.
5. What are the latest advancements in mitochondrial-targeted therapies for age-related diseases, and how do they impact cellular bioenergetics?
Emerging therapies include mitochondrial peptides (like SS-31), NAD+ boosters, mitophagy inducers, and gene-editing approaches targeting mitochondrial DNA. These interventions aim to restore bioenergetic efficiency, reduce oxidative damage, and improve cellular resilience against aging-related decline.
Key References for Further Reading
- Mitochondrial dynamics mechanisms (Nature, 2023)
- mtH2S healthspan effects (PNAS, 2023)
- Critical analysis of MFRTA (PMC, 2013)
- Mitochondrial signaling pathways (JCI, 2012)
- Conserved longevity pathways (PubMed, 2019)
- Sex hormones and mitochondria (PMC, 2014)
- Mitochondrial DNA mutations review (Biomed, 2016)